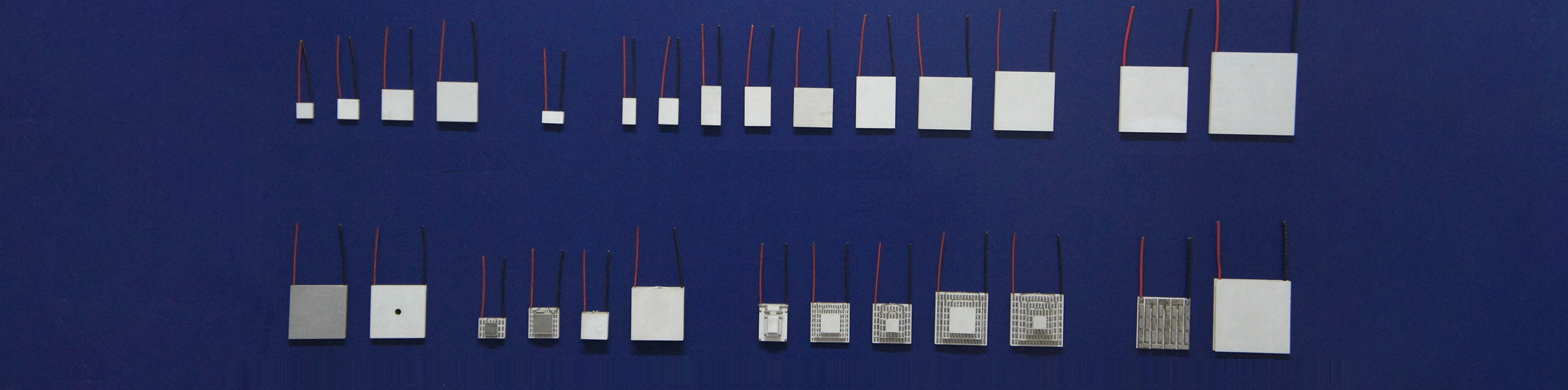
Thermoelectric cooling unit ,peltier cooler(also known as thermoelectric cooling components) are solid-state cooling devices based on the Peltier effect. They have the advantages of no mechanical movement, no refrigerant, small size, fast response, and precise temperature control. In recent years, their applications in consumer electronics, medical care, automobiles and other fields have continued to expand.
I. Core Principles of thermoelectric cooling system and components
The core of thermoelectric cooling is the Peltier effect: when two different semiconductor materials (P-type and N-type) form a thermocouple pair and a direct current is applied, one end of the thermocouple pair will absorb heat (cooling end), and the other end will release heat (heat dissipation end). By changing the direction of the current, the cooling end and the heat dissipation end can be interchanged.
Its cooling performance mainly depends on three core parameters:
Thermoelectric coefficient of merit (ZT value) : It is a key indicator for evaluating the performance of thermoelectric materials. The higher the ZT value, the higher the cooling efficiency.
The temperature difference between the hot and cold ends: The heat dissipation effect at the heat dissipation end directly determines the cooling capacity at the cooling end. If the heat dissipation is not smooth, the temperature difference between the hot and cold ends will narrow, and the cooling efficiency will drop sharply.
Working current: Within the rated range, an increase in current enhances the cooling capacity. However, once the threshold is exceeded, the efficiency will decrease due to an increase in Joule heat.
II The development history and technological breakthroughs of thermoelectric cooling units(peltier cooling system)
In recent years, the development of thermoelectric cooling components has focused on two major directions: material innovation and structural optimization.
Research and development of high-performance thermoelectric materials
The ZT value of traditional Bi₂Te₃ -based materials has been increased to 1.2-1.5 through doping (such as Sb, Se) and nanoscale treatment.
New materials such as lead telluride (PbTe) and silicon-germanium alloy (SiGe) perform exceptionally well in medium and high-temperature scenarios (200 to 500℃).
New materials such as organic-inorganic composite thermoelectric materials and topological insulators are expected to further reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Component structure optimization
Miniaturization design: Prepare micron-scale thermopiles through MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology to meet the miniaturization requirements of consumer electronics.
Modular integration: Connect multiple thermoelectric units in series or parallel to form high-power thermoelectric cooling modules, peltier coolers,peltier devices, meeting industrial-grade thermoelectric cooling requirements.
Integrated heat dissipation structure: Integrate the cooling fins with the heat dissipation fins and heat pipes to enhance heat dissipation efficiency and reduce the overall volume.
III Typical application scenarios of thermoelectric cooling units, thermoelectric cooling components
The greatest advantage of thermoelectric cooling units lies in their solid-state nature, noise-free operation, and precise temperature control. Therefore, they hold an irreplaceable position in scenarios where compressors are not suitable for cooling.
In the field of consumer electronics
Mobile phone heat dissipation: High-end gaming phones are equipped with micro thermoelectric cooling modules, TEC modules, peltier devices, peltier modules, which, in combination with liquid cooling systems, can quickly lower the chip temperature, preventing frequency reduction due to overheating during gaming.
Car refrigerators,Car coolers: Small car refrigerators mostly adopt thermoelectric cooling technology, which combines cooling and heating functions (heating can be achieved by switching the current direction). They are small in size, low in energy consumption, and compatible with the 12V power supply of a car.
Beverage cooling cup/insulated cup: The portable cooling cup is equipped with a built-in micro cooling plate, which can quickly cool beverages to 5 to 15 degrees Celsius without relying on a refrigerator.
2. Medical and biological fields
Precise temperature control equipment: such as PCR instruments (polymerase chain reaction instruments) and blood refrigerators, require a stable low-temperature environment. Semiconductor refrigeration components can achieve precise temperature control within ±0.1℃, and there is no risk of refrigerant contamination.
Portable medical devices: such as insulin refrigeration boxes, which are small in size and have a long battery life, are suitable for diabetic patients to carry when going out, ensuring the storage temperature of insulin.
Laser equipment temperature control: The core components of medical laser treatment devices (such as lasers) are sensitive to temperature, and the semiconductor cooling components can dissipate heat in real time to ensure the stable operation of the equipment.
3. Industrial and aerospace fields
Industrial small-scale refrigeration equipment: such as electronic component aging test chambers and precision instrument constant temperature baths, which require a local low-temperature environment, thermoelectric cooling units, thermoelectric components can be customized with refrigeration power as needed.
Aerospace equipment: Electronic devices in spacecraft have difficulty dissipating heat in a vacuum environment. Thermoelectric cooling systems, thermoelectric cooling units, thermoelectric components, as solid-state devices, are highly reliable and vibration-free, and can be used for temperature control of electronic equipment in satellites and space stations.
4. Other emerging scenarios
Wearable devices: Smart cooling helmets and cooling suits, with built-in flexible thermoelectric cooling plates, can provide local cooling for the human body in high-temperature environments and are suitable for outdoor workers.
Cold chain logistics: Small cold chain packaging boxes, powered by thermoelectric cooling, peltier cooling and batteries, can be used for short-distance transportation of vaccines and fresh produce without relying on large refrigerated trucks.
IV. Limitations and Development Trends of thermoelectric cooling units, peltier cooling components
Existing limitations
The cooling efficiency is relatively low: Its energy efficiency ratio (COP) is usually between 0.3 and 0.8, which is much lower than that of compressor cooling (COP can reach 2 to 5), and is not suitable for large-scale and high-capacity cooling scenarios.
High heat dissipation requirements: If the heat at the heat dissipation end cannot be discharged in time, it will seriously affect the cooling effect. Therefore, it must be equipped with an efficient heat dissipation system, which limits the application in some compact scenarios.
High cost: The preparation cost of high-performance thermoelectric materials (such as nano-doped Bi₂Te₃) is higher than that of traditional refrigeration materials, resulting in a relatively high price of high-end components.
2. Future development trends
Material breakthrough: Develop low-cost, high-ZT value thermoelectric materials, with the goal of increasing the room-temperature ZT value to over 2.0 and narrowing the efficiency gap with compressor refrigeration.
Flexibility and integration: Develop flexible thermoelectric cooling modules,TEC modules ,thermoelectric modules,peltier devices,peltier modules,peltier coolers, to adapt to curved surface devices (such as flexible screen mobile phones and smart wearable devices); Promote the integration of thermoelectric cooling components with chips and sensors to achieve “chip-level temperature control”.
Energy-saving design: By integrating Internet of Things (iot) technology, intelligent start-stop and power regulation of the cooling components are achieved, reducing overall energy consumption.
V. Summary
Thermoelectric cooling units, peltier cooling units, thermoelectric cooling systems, with their unique advantages of being solid-state, silent and precisely temperature-controlled, occupy an important position in fields such as consumer electronics, medical care and aerospace. With the continuous upgrading of thermoelectric material technology and structural design, the issues of its cooling efficiency and cost will gradually improve, and it is expected to replace traditional cooling technology in more specific scenarios in the future
Post time: Dec-12-2025